scikit-learnによる機械学習プログラミング入門
前処理:データの準備
scikit-learnに同梱されているirisデータセットを使う。
from sklearn import datasets
import numpy as np
iris = datasets.load_iris()
print(iris.DESCR)
.. _iris_dataset:
Iris plants dataset
--------------------
**Data Set Characteristics:**
...
irisデータセットの中身を見る。
import pandas as pd
iris_df = pd.DataFrame(iris.data, columns=iris.feature_names)
iris_df['species'] = [iris.target_names[i] for i in iris.target]
iris_df.sample(10)
| sepal length (cm) | sepal width (cm) | petal length (cm) | petal width (cm) | species | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.9 | 3.0 | 1.4 | 0.2 | setosa |
| 124 | 6.7 | 3.3 | 5.7 | 2.1 | virginica |
| 147 | 6.5 | 3.0 | 5.2 | 2.0 | virginica |
| 95 | 5.7 | 3.0 | 4.2 | 1.2 | versicolor |
| 39 | 5.1 | 3.4 | 1.5 | 0.2 | setosa |
| 19 | 5.1 | 3.8 | 1.5 | 0.3 | setosa |
| 42 | 4.4 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 0.2 | setosa |
| 27 | 5.2 | 3.5 | 1.5 | 0.2 | setosa |
| 18 | 5.7 | 3.8 | 1.7 | 0.3 | setosa |
| 93 | 5.0 | 2.3 | 3.3 | 1.0 | versicolor |
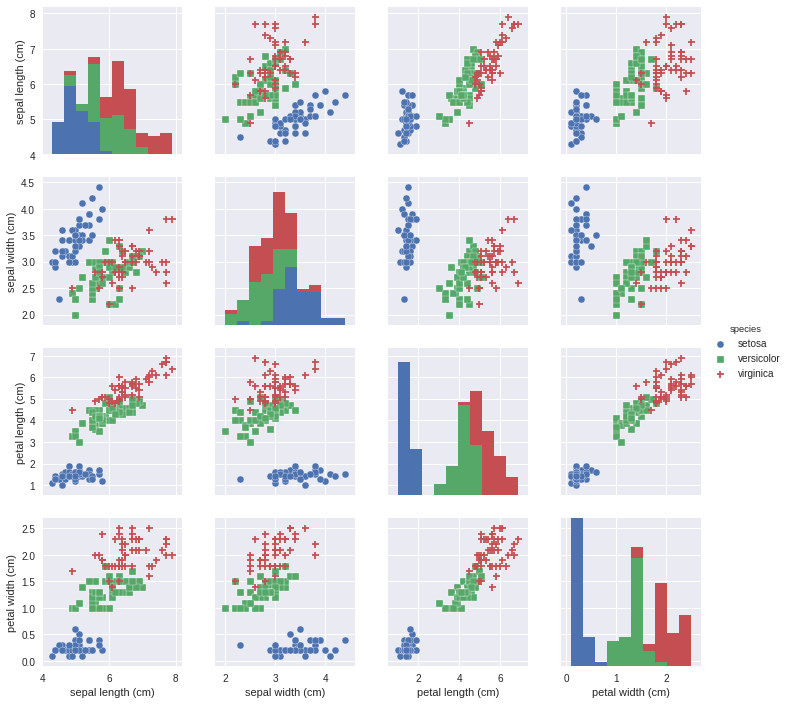
irisデータセットの分布を眺める。
import seaborn as sns
sns.pairplot(iris_df, hue='species', markers=["o", "s", "D"])
特徴選択:petal lengthとpetal width ([2, 3]) を特徴量として使うことにする。
X = iris.data[:, [2, 3]]
y = iris.target
print('Class labels:', np.unique(y))
Class labels: [0 1 2]
前処理:データの分割
トレーニングデータとテストデータに分割する。
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=1, stratify=y)
print('Labels counts in y:', np.bincount(y))
print('Labels counts in y_train:', np.bincount(y_train))
print('Labels counts in y_test:', np.bincount(y_test))
Labels counts in y: [50 50 50]
Labels counts in y_train: [35 35 35]
Labels counts in y_test: [15 15 15]
前処理:スケーリング
StandardScalerを使って、平均0 分散1となるようにデータをスケーリングする。
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
sc = StandardScaler()
sc.fit(X_train)
X_train_std = sc.transform(X_train)
X_test_std = sc.transform(X_test)
学習:トレーニングデータによる予測モデル学習
パーセプトロンと呼ばれるある学習アルゴリズムにより学習
from sklearn.linear_model import Perceptron
ppn = Perceptron(max_iter=40, tol=1e-3, eta0=0.1, random_state=1234)
ppn.fit(X_train_std, y_train)
Perceptron(alpha=0.0001, class_weight=None, early_stopping=False, eta0=0.1,
fit_intercept=True, max_iter=40, n_iter=None, n_iter_no_change=5,
n_jobs=None, penalty=None, random_state=1234, shuffle=True,
tol=0.001, validation_fraction=0.1, verbose=0, warm_start=False)
他に使用可能なアルゴリズム(一部)
- k最近傍法 (sklearn.neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier)
- ロジスティック回帰 (sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression)
- サポートベクタマシン (sklearn.svm.SVC)
- ランダムフォレスト (sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestClassifier)
評価:テストデータによる精度評価
テストデータにおける精度(的中率)を計算する。
y_pred = ppn.predict(X_test_std)
print('Misclassified samples: %d' % (y_test != y_pred).sum())
Misclassified samples: 1
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
print('Accuracy: %.2f' % accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
Accuracy: 0.98
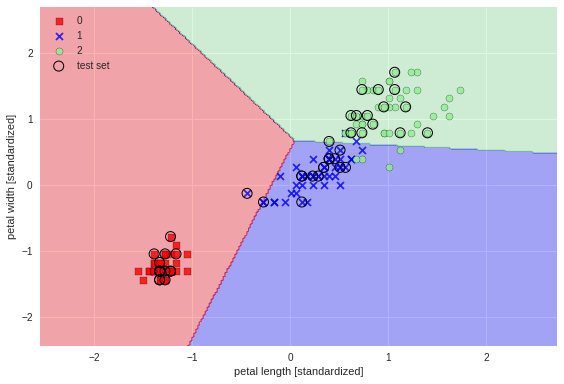
評価:予測モデルの可視化
予測モデルの線形関数を散布図にプロットする。
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_decision_regions(X, y, classifier, test_idx=None, resolution=0.02):
# setup marker generator and color map
markers = ('s', 'x', 'o', '^', 'v')
colors = ('red', 'blue', 'lightgreen', 'gray', 'cyan')
cmap = ListedColormap(colors[:len(np.unique(y))])
# plot the decision surface
x1_min, x1_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
x2_min, x2_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx1, xx2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x1_min, x1_max, resolution),
np.arange(x2_min, x2_max, resolution))
Z = classifier.predict(np.array([xx1.ravel(), xx2.ravel()]).T)
Z = Z.reshape(xx1.shape)
plt.contourf(xx1, xx2, Z, alpha=0.3, cmap=cmap)
plt.xlim(xx1.min(), xx1.max())
plt.ylim(xx2.min(), xx2.max())
for idx, cl in enumerate(np.unique(y)):
plt.scatter(x=X[y == cl, 0],
y=X[y == cl, 1],
alpha=0.8,
c=colors[idx],
marker=markers[idx],
label=cl,
edgecolor='black')
# highlight test samples
if test_idx:
# plot all samples
X_test, y_test = X[test_idx, :], y[test_idx]
plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0],
X_test[:, 1],
facecolor='none',
edgecolor='black',
alpha=1.0,
linewidth=1,
marker='o',
s=100,
label='test set')
X_combined_std = np.vstack((X_train_std, X_test_std))
y_combined = np.hstack((y_train, y_test))
plot_decision_regions(X=X_combined_std, y=y_combined,
classifier=ppn, test_idx=range(105, 150))
plt.xlabel('petal length [standardized]')
plt.ylabel('petal width [standardized]')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.tight_layout()